Coordinate Measurement Machines (CMMs) are used to automatically measure points on a part to verify that its dimensions and geometry match the design intent and drawing specifications.
What is a Coordinate Measurement Machine?
A Coordinate Measurement Machine (CMM) is a multi-axis measurement machine used to accurately measure points on a component’s surface. The points are then processed to verify that the component’s size and shape meet the design specifications on the associated drawing or in its model-based definition (MBD). CMMs run scrips or “programs”, which contain instructions about how and where to measure points, how to process the data, and the report to be generated once completed.
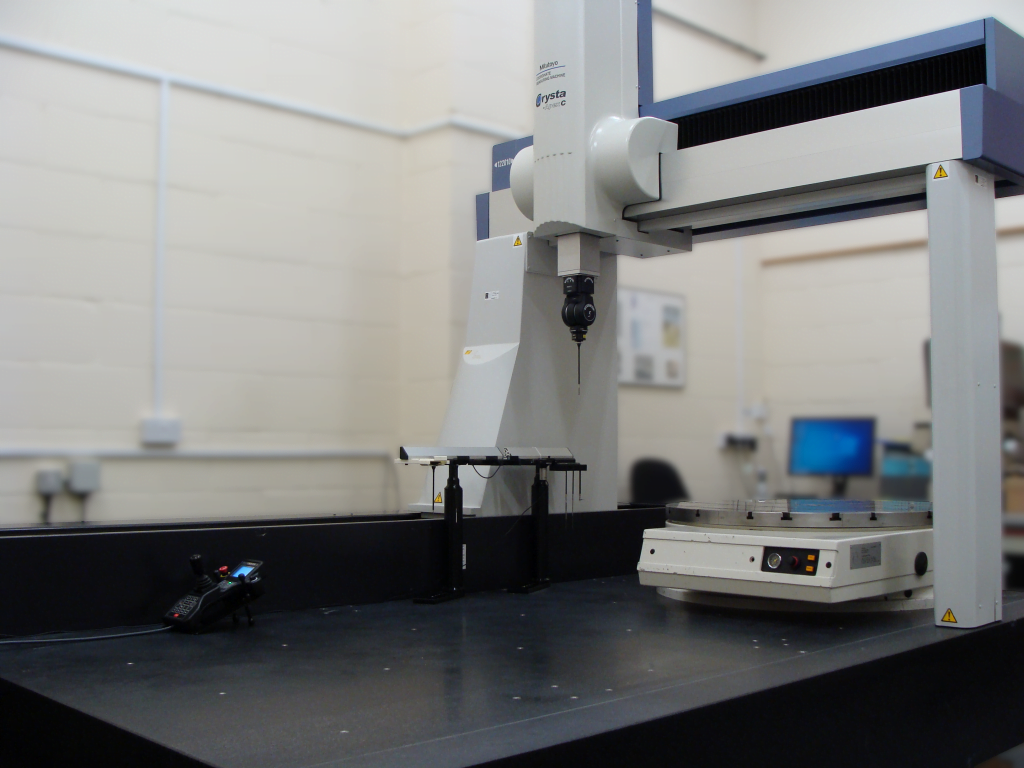
There are many variations and types of CMMs, however the most common type is the traditional bridge CMM. This has three linear axes which move perpendicular to each other (XYZ). Points are normally measured using a touch or scanning probe, mounted on a pivoting head attached to the vertical axis. A pivoting head gives two additional axes (A&B) which enables measurement of more complex designs. Rotary tables can also instead of or in addition to pivoting heads for rotating parts to increase access to features that may otherwise be unreachable. Rotary tables can also be used for optimising the cycle time on circular parts.
Part measurement is usually done using automated (CNC) programs, although it is also possible to use manual mode. The program sends instructions to the machine to move each axis, controlling the probe tip position and orientation to measuring points. The measured points can then be used to check the distance between features and analyse geometric properties such as hole positions, perpendicularity, parallelism etc.
Why use a CMM?
The three key drivers for using a CMM over other methods of inspection are:
– Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) requirements
– Automation requirements
– Accuracy requirements
Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) Requirements
Geometric features such as hole positions, flatness, circularity etc. can be difficult and impractical to measure by other methods. CMMs are ideal for assessing GD&T requirements and allow for a full dimensional inspection to be carried out.
Automation Requirements
CMMs can be setup to run fully automated programs, which probe the part, process the data and produce detailed reports. The process can be setup to be completely automated and operator independent, making them ideal for in process inspection & monitoring on production lines. In this capacity, they provide invaluable visibility of the manufacturing process’s performance and stability.
Accuracy requirements
CMMs can be calibrated to traceable standards with a baseline accuracy of just a few microns, with the very best achieving submicron calibrations. This makes them the most accurate way to measure dimensions and geometrics on a wide range of components. Other methods such as interferometry are capable of submicron measurements, but they lack the flexibility to measure a wide array of parts and geometric features like a CMM.
